Conditional statement (if-else)
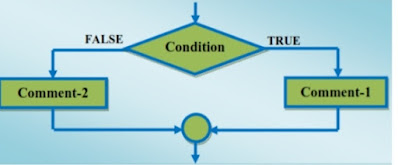
In conditional control , the execution of statements depends upon the condition-test. If the condition evaluates to true, then a set of statements is executed otherwise another set of statements is followed. This control is also called Decision Control because it helps in making decision about which set of statements is to be executed.
If condition
The if statement is the most simple decision making statement in C++ programming. Using if statement we test some condition, if the condition is true then a block of statements is executed otherwise not. Let's take an example :-
If(condition){
//body
}
In the above syntax inside the brackets ( ) of if statement we will write our condition. If the condition is true then the statements written within the curly braces { } of if statement will execute otherwise not. We can write our condition using Arithmetic, Relational and Logical operators.
Else-if Condition
When a piece of code needs to be evaluated based on several different conditions, the “if…else if…else” statement is used. While deciding between two options, the if-else statement is utilized to execute a segment of code. The “if…else if…else” statement is used, however, when we must choose amongst multiple possibilities. Although there is only one “if” and one “else” in this control framework, there can be several else-if blocks. Let's take an example :-
If(condition){
//body
}else If(condition){
//body
}else{
}
Else condition
When the if & else-if statements not satisfying the condition, then the solution given in else part is taken as Output or final solution.
Let us take an example of else statement.
If(condition){
//body
}else If(condition){
//body
}else{
//body
}
let's take an example of a program which gives the greater number between two given numbers :-
Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( ){
int a, b;
cin>>a>>b;
if(a>b){
cout<<"a is greater";
}
else If(a==b){
cout<<"both are equal ";
}
else{
cout<<"b is greater ";
}
return 0;
}
Instagram 👇
Comments
Post a Comment